DISCOVERIES REPORTS (ISSN 2393249X), 2021, volume 4
Access FULL text of the manuscript here: Full text (PDF)
CITATION: Miglani S, Ansari I, Boreak N, Vadav V. Integrated approach for management of oro-dental manifestations in survivors of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Discoveries Reports, 2021; 4: e23. DOI: 10.15190/drep.2021.8 Submitted: May 19, 2021; Revised: June 21, 2021; Accepted: June 30, 2021; Published: 2021;
Integrated approach for management of oro-dental manifestations in survivors of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Sanjay Miglani (1), Irfan Ansari (1), Nezar Boreak (2), Vijay Vadav (1,*)
(1) Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India
(2) Department of Restorative Dental Sciences, College of Dentistry, Jazan University, Jazan, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
* Corresponding author: Vijay Vadav, Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, 110025, India; Email: dr.vjyadav@gmail.com
Abstract
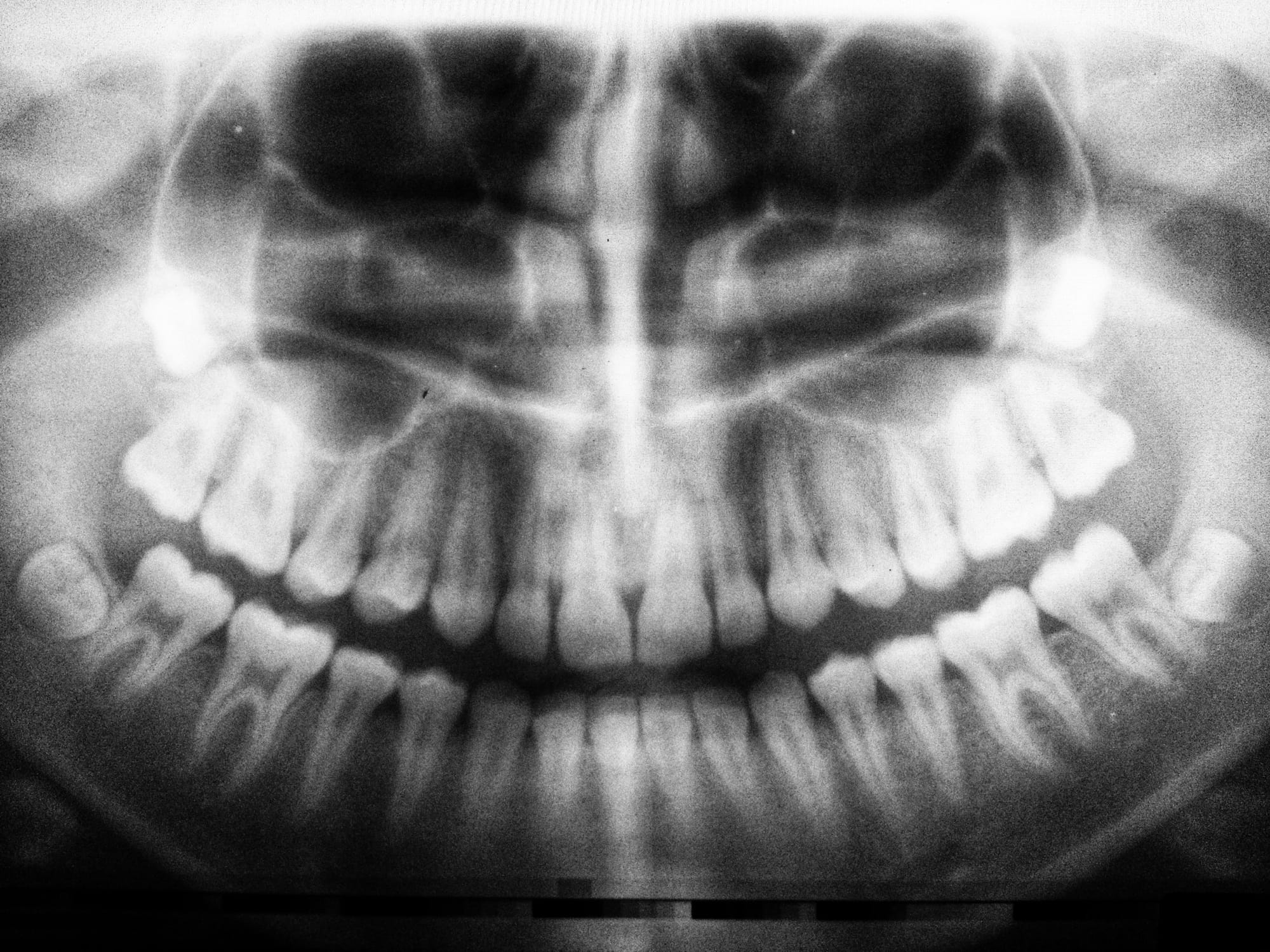
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis are severe muco-cutaneous reactions seen in clinical practice, usually due to adverse reactions to certain drugs, such as sulfonamides, anticonvulsants, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are characterized by the eruption of blisters and epithelial sloughing, which can turn into a life-threatening situation. Acute and chronic complications of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis are well documented in the literature, and it is recognized that survivors may develop oro-dental abnormalities as a long-term complication of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. To date and to our knowledge, there is no publication available emphasizing the importance of an integrated approach amongst dental specialties for the management of oro-dental complications of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. This review aims to provide an update on a wide range of oro-dental sequelae as a long-term complication following an acute episode of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, along with an emphasis on the need of an interdisciplinary collaboration of dental specialties for early diagnosis and management of such cases.
References
1. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 10;331(19):1272–85.
2. Roujeau JC, Guillaume JC, Fabre JP, Penso D, Fléchet ML, Girre JP. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome). Incidence and drug etiology in France, 1981-1985. Arch Dermatol. 1990 Jan;126(1):37–42.
3. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Jan;129(1):92–6.
4. Yang M-S, Lee JY, Kim J, Kim G-W, Kim B-K, Kim J-Y, et al. Incidence of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Database in Korea. PLoS One. 2016; 11(11): e0165933.
5. Lee HY, Walsh SA, Creamer D. Long-term complications of Stevens–Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN): the spectrum of chronic problems in patients who survive an episode of SJS/TEN necessitates multidisciplinary follow-up. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177(4):924–35.
6. Bequignon E, Duong TA, Sbidian E, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Chatelin V, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: ear, nose, and throat description at acute stage and after remission. JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Mar;151(3):302–7.
7. Revuz J, Penso D, Roujeau JC, Guillaume JC, Payne CR, Wechsler J, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical findings and prognosis factors in 87 patients. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Sep;123(9):1160–5.
8. Oplatek A, Brown K, Sen S, Halerz M, Supple K, Gamelli RL. Long-term follow-up of patients treated for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res Off Publ Am Burn Assoc. 2006 Feb;27(1):26–33.
9. Sedghizadeh PP, Kumar SKS, Gorur A, Mastin C, Boros AL. Toxic epidermal necrolysis with a rare long-term oral complication requiring surgical intervention. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008 Apr;105(4):e29-33.
10. Royan SJ. Lip adhesion: unusual complication of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Off J Am Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Apr;68(4):901–3.
11. Gaultier F, Rochefort J, Landru M-M, Allanore L, Naveau A, Roujeau J-C, et al. Severe and unrecognized dental abnormalities after drug-induced epidermal necrolysis. Arch Dermatol. 2009 Nov;145(11):1332–3.
12. Roujeau JC, Phlippoteau C, Koso M, Wechsler J, Andre C, Binaghi M, et al. Sjögren-like syndrome after drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lancet Lond Engl. 1985 Mar 16;1(8429):609–11.
13. Chosidow O, el Wady Z, Devanlay M, Jaffray P, Revuz J, Roujeau JC. Hyperamylasemia in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Jun;129(6):792–3.
14. De Man K. Abnormal root development, probably due to erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome). Int J Oral Surg. 1979 Oct;8(5):381–5.
15. Ranalli DN, Elliott MA, Whaley TM, Campagna ED Jr. Stevens-Johnson syndrome: report of case with abnormal root development. ASDC J Dent Child. 1984 Jul-Aug;51(4):298-301.
16. Brook U. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and abnormal root development: a case report. Int J Paediatr Dent. 1994;4(2):101–3.
17. Bajaj N, Madan N, Rathnam A. Cessation in root development: Ramifications of ‘Stevens-Johnson’ syndrome. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2012 Jul 1;30(3):267.
18. Sangwan A, Saini H-R, Sangwan P, Dahiya P. Stunted root development: A rare dental complication of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Clin Exp Dent. 2016;8(4):e462–4.
19. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: A Case Report. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent. Accessed in 2021. Available from: http://journal.kapd.org/journal/view.php?number=1549
20. Barea-Jiménez N, Calero J, Molina-Negrón D, López Del-Valle LM. Treatment for oral lesions in pediatric patients with Stevens-Johnson’s syndrome: A case report and literature review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2020 Jul;30(4):489–96.
21. Valladares Neto J, Rino Neto J, de Paiva JB. Orthodontic movement of teeth with short root anomaly: Should it be avoided, faced or ignored? Dent Press J Orthod. 2013 Dec;18(6):72–85.
22. Vishwanath M, Chen P-J, Upadhyay M, Yadav S. Orthodontic management of a patient with short root anomaly and impacted teeth. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop Off Publ Am Assoc Orthod Its Const Soc Am Board Orthod. 2019 Mar;155(3):421–31.